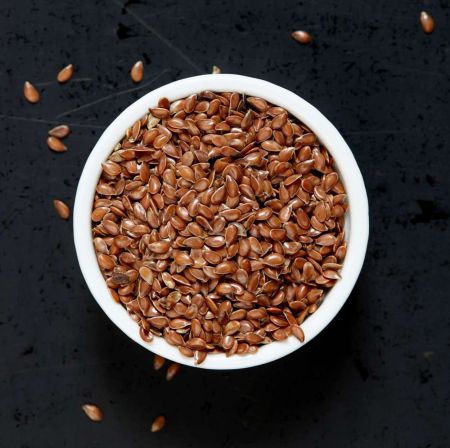
Sultan
A sultan is a title of authority in certain Islamic countries, historically used to denote rulers or leaders, particularly in the Middle East and North Africa. The term suggests a sovereign power and has been associated with various dynasties and empires. Sultans often governed extensive territories and held significant political, military, and religious influence. While the role of the sultan has evolved over time, in some regions today, the title still carries cultural and historical significance, reflecting a connection to the past.
₹ 490.00
₹500
(Inclusive of all taxes)
-

No Warranty
-
COD Avilable
-
Returnable
-
Non cancelable
About this item
A sultan is a sovereign ruler, often associated with Islamic states or kingdoms. The title originates from the Arabic word "sulat," meaning authority or power. Historically, sultans governed vast empires, and their reigns were marked by significant cultural, economic, and political development.
Sultans typically held absolute power and often ruled with the support of a council or advisors. They were responsible for upholding Islamic law (Sharia) and maintaining order in their realms. The governance style varied widely, with some sultans being more benevolent and enlightened, while others were more despotic and authoritarian.
Sultans are commonly associated with opulent palaces, grandiose ceremonies, and rich cultural patronage, influencing art, architecture, literature, and science. Their courts often served as centers of learning and culture, attracting scholars, poets, and artists.
In modern contexts, the title "sultan" is still used in some countries, such as Brunei and Oman, where the rulers maintain significant political and religious authority, guiding their nations while balancing tradition with contemporary governance.
A sultan is a sovereign ruler, often associated with Islamic states or kingdoms. The title originates from the Arabic word "sulat," meaning authority or power. Historically, sultans governed vast empires, and their reigns were marked by significant cultural, economic, and political development.
Sultans typically held absolute power and often ruled with the support of a council or advisors. They were responsible for upholding Islamic law (Sharia) and maintaining order in their realms. The governance style varied widely, with some sultans being more benevolent and enlightened, while others were more despotic and authoritarian.
Sultans are commonly associated with opulent palaces, grandiose ceremonies, and rich cultural patronage, influencing art, architecture, literature, and science. Their courts often served as centers of learning and culture, attracting scholars, poets, and artists.
In modern contexts, the title "sultan" is still used in some countries, such as Brunei and Oman, where the rulers maintain significant political and religious authority, guiding their nations while balancing tradition with contemporary governance.
0 Review Of Product Sultan













